Enhancing Work Climate to Improve the Perceived Performance Leading to Talent Retention-A Study of Pakistani Service Sector
Muhammad Mujtaba1*
Sadaf Jamal2
1,2PhD- Management Sciences at SZABIST, Karachi, Pakistan |
AbstractImproved perceived performance and talent retention are great challenges for most of the organizations in the world, and leading organizations of today are stating that the human is most important resource for them behind their success but beside this, it is tough job for management of organization to manage human in organizational work climate which is combination of different factors towards improve perceived performance and talent retention. The intention of this research was to evaluate the influence of different factors of organizational work climate on improvement of perceived performance leading to talent retention in services sector firms of Pakistan. Five major factors pertain to organizational work climate were taken as independent variables such as role clarity, relevant nature of work, teamwork, rewards and fairness. This research work was limited to conduct quantitative survey through close ended questionnaire from sample size of 201 Manager Operations of commercial banks of Pakistan. Philosophy stance of positivism is used whereas statistical test of correlation, regression and sobel are used to for analysis the relations and impact of variable. The finding indicated that there is significant role of work climate on improvement of perceived performance leading to talent retention. |
Licensed: |
|
Keywords: |
|
| (* Corresponding Author) |
1. Introduction
Employee performance and talent retention are great challenges for most of the firms in the world and successful organizations of today are stating that the human is most important asset for them behind their success. These organizations are constantly improving their work climate towards build a good image of their employment brand to attract existing employees and talent of other firms to survive in global talent war.
In past people look for companies who can hire them for work, but now in the age of innovation, the organizations are looking for people. This is a century where work is distinguished by unprecedented stages of talent movements, where employees are want to fulfil their own personal desires, which lead to increasing apprehension among organizations concerning the employees’ retention. At its heart, the management of employee performance and talent retention are just issue of job satisfaction, which means it is matter of anticipating the need in favour of human capital and then fixing out a strategy to meet it. These situations emphasized to researchers to review the factors which influence on employees’ job satisfaction towards improve the perceived performance and talent retention (Cappelli, 2008).
The job satisfaction of employee is complex phenomenon and many research studies have conducted, where scholars have discussed numerous definitions and factors involved in employee job satisfaction such as: compensation, fringe benefits, work climate, job security, retirement benefits, health facilities, career development, trainings, recognition of work, supervisor behavior, work autonomy, team work, size and structure, effective communication, safe working environment, lenient working hours, insurance facilities, location of work station, nature of work, promotion, rewards and others. Whereas in some cases it has been also seen that job dissatisfaction create mental health disorder which includes, anxiety, alcohol, depression, abuse and many other serious kind on health diseases which ultimately affect the performance of employee. Absence of job satisfaction and presence of other opportunities in the organization ultimately leads to decrease in job performance and increase in turnover (Lumley, Coetzee, Tladinyane, & Ferreira, 2011).
According to Irshad and Afridi (2007) money bring individuals in the their organizations but it is not necessary that they should remain in their organizations only because of money, most of time work climate perform major role behind their stay in company.
This is a century of modernization and competition which compel every organization to bring new products in market as per demand of their customers to survive in competition. This scenario has realized to organizations that human is one of important asset and talent is competitive advantage of their organizations. To face this situation, the different services provider organizations of the world are working on different patterns towards job satisfaction of employees to improve perceived performance leads to talent retention such as employee need, organization culture, labour demand and supply, competition, economy and others. Losing of productive “Star” worker is like losing number of potential customers, therefore, the organizations are requited remain conscious and create better work climate at workplace to improve perceived performance of employees and retain star workers for longer period (Siebert & Zubanov, 2009).
The unemployment is very high in many counties even which includes America (United States) but these countries are facing problem of talent shortage and it will increase in next decade and ultimately this shortage will compel the companies to limit their business, in fact, it will be tough for most of the companies to survive in global competition, thus, there is need that companies should create better work climate to improve the performance of employees and talent retention (McMullen, Scott, & Royal, 2012).
Today, in Pakistan, the Banking Sector (Service sector) has accepted the importance of human resources for their success and survival, and banking firms have started to enhance their work climate of organizations through different way to motivate the employees so that perceived performance should be achieved as well as employees may remain in organizations. Various research studies have been done by different scholars on relationship between work climate and perceived performance and talent retention. However, in most of such kind of studies the researchers focused only two or three aspects of work climate towards improve the perceived performance and talent retention, or mostly these studies only emphasized on compensation, fringe benefits or training factors of work climate. But this research study is focused on five most important factors of work climate to improve perceived performance leading to talent retention in service sector organizations, it includes: role clarity, relevant nature of work, teamwork, rewards and fairness to see the impact and relationship of these work climate factors on perceived performance leading to talent retention.
Role clarity is one of the important elements of work climate which support employees to work in a systemic way with full job satisfaction towards achieve the organizational goals. In most of the organizations the employees don’t have clear role, responsibilities and reporting officer, and due to this the employees of these firms are working in ambiguity and matrix reporting system which create mental stress and job dissatisfaction at most of the time.
Relevant nature of work is another important factor of work climate of the organization which is based on idea of the right person, at right place and right time. Most of the time, the organizations don’t assign the right task to right person means many of the tasks of organization assign to those individuals who don’t have their field of expertise or interests or beyond their capacity, thus, this situation also creates dissatisfaction among employees.
Teamwork is also essential factor of work climate which creates close interaction and better communication among employees where every employee learn new things from other employee and combine team efforts resolve the problem in professional way and build new ideas and innovation in tough competition. In teamwork process the level of employees satisfaction increases when their reporting officer listen and understand them and shows his interest in their work and their expectation from organization in return of their performance (Lumley et al., 2011) .
Rewards on performance (Monitory benefit) are also one of the significant elements of work climate which encourages employees to perform better than before. Many organizations don’t recognize the outstanding performance of employees or if they recognize, then they only recognize in words or in shape of issuing appreciation certificates. The outstanding employee always looks forward for some special advantage in terms of monitory benefit against his special achievement.
Most of the organizations the top management gives special care to their favourite employees and provide them different additional facilities and promotions without evaluating their performance with honesty, and violate the procedures as well as policies of organization which create the job dissatisfaction among performer or talent. When employees are treated as unfair or inequity basis then they demoralized and they put fewer efforts in their assigned tasks. Performer are very much conscious about fairness of procedures and policies at work environment, it affects their intention and emotions whenever they treated unfair such as anger, guilt, dissatisfaction and others, but when they are treated fair on basis of their output then they feel comfortable and show their full loyalty & commitment and desire to stay further in the company (Irshad & Afridi, 2007) .
1.2. Research Purpose
Performance and talent retention are great challenges for most of the organizations of world which also include Pakistan. The purpose of conducting this study was to assess the role of enhancing work climate in firms of services sector towards improve the perceived performance leading to talent retention.
The following are the research questions of the study:
Q.No.1.What is impacts of enhancing work climate to improve perceived performance leading to talent retention?
Q.No.2.Which factor of work climate is most important in improving of perceived performance leading to talent retention?
Q. No.3. Which factor of work climate has low impact on improving perceived performance leading to talent retention?
1.3. Research Objectives
The following are the research objects:
- To evaluate the role of work climate towards improve perceived performance leading to talent retention.
- To determine that which factor of work climate has more impact on improvement of perceived performance leading to talent retention.
- To determine that which factor of work climate has low impact on improving perceived performance leading to talent retention?
1.4. Justification, Limitation and Scope
Ample of research work has been done on work climate but this kind of work has never been done so for in context of enhancing work climate to improve perceived performance leading to talent retention in services sector organizations (i.e. Banking Sector) of Pakistan.
Stakeholders of this particular research studies are banking firms and all those services sector organization which are located in Pakistan, it includes government or non government, national or international , business and research, consultants, students and scholars.
This research work is limited to work climate of commercial banks (Manager Operations positions) which are operating their business in Pakistan.
2. Literature Review
The literature review pertain to title of this research study across the world acknowledges that leading organizations mainly focusing on work climate to improve the perceived performance and talent retention. Human Resources Department activities of every organization mainly consisting of three stages such as entry of employee, management of employee and exit of employee, firstly, the entry stage of employee in organization include recruitment and selection of qualified candidates and provide him necessary orientation and different trainings to enhance his skills and abilities to perform assigned tasks in professional way, second stage include such as management and performance of employees in organization, this stage is very important where employee expected to perform his duties with commitments and show his loyalty toward achieve the organizational goals, at this stage organization provide good working climate to employee toward his job satisfaction, because with job satisfaction , the employee always perform his duties with full dedication and avoid to leave employer, whereas in third stage of employee exit is mainly depending on employee dissatisfaction from second stage which is management of employee means provision of good working climate within organization. Many scholars have done the research on importance of work climate and describe different factors of work climate as explained below (Putter, 2010).
According to Putter (2010) the work climate is the perception that what organization wants in term of procedures, policies, practices, routines and rewards, based on organizational members whereas procedures, policies, practices, routines and rewards are integrated parts of department of human resources of every organization.
Richardson (2008) founds that managers and supervisors are using different tools for job satisfaction of employees because significant profit portions of firm is correlated with performance of employees and retention, for example, only in America, due to dissatisfaction of employees the American businesses looses their productivity and cost of that lost was $ 300 (billion) in a year, and now the situation of external factors such as change of economic environment, intensive competition in markets and technology advancement have developed the huge pressure on management to rethink that how they should handle their workforce and the factors which affects workers.
According to Putter (2010) the basic difference between climate and culture is that the culture of organization refer to the essential organization structure which sets in beliefs, values & assumptions of the members of organization, whereas, organizational climate is reflected into procedures and practices which are observable or can be seen in organization, and climate of organization direct affect to outcomes or performance of individual which can be easily compared. Organizational climate focused on day to day interaction behavior of employees within the firm, and climate is basically decided through managerial assumptions as well as the work relationship between line managers & their subordinates, it define in terms of policies and procedures of organization, employee value, personalities & needs, team work and rewards (Tsai, 2014).
Olakitan and Ayobami (2011) he explained that before setting the parameters of job satisfaction, it is very important to understand the behavior of individuals (which vary from individual to individual), because job satisfaction is cognitive process which can’t be seen openly, but it can be seen in behavior, the organization must develop strategy to enhance the work climate which best fit in the organization and every individual should feel happy and shows his commitment as well as loyalty with the organization, and put his extra efforts towards increase the market share of the organization.
Work climate is one of leading factor determining intra-organizational interaction and attitudes of individual which ultimately impact on individual work satisfaction and organization goals, and there are nine types of effects such as company profit, self interest, friendship, efficiency, social responsibility, team interest, personal morality, rules & procedures, professional and laws codes (Elçi & Alpkan, 2009).
In services sector, the internal climate of organization is more important as compare to production sector, it is internal work climate in services sector which positively or negatively influence on attitudes and perceptions of employees, positive internal climate will encourage to consistent high levels of delivery of service quality, the significance or importance of quality of service is more sensitive in connection of banking industry, where contact between employees and customers is high, and employees are key element in operational process of a success in banking industry, therefore organizations must establish and maintain encouraging work climate for employees toward effectively deliver outstanding service, and it is big challenge for management to how organization should establish an environment which supports workers in delivery of quality service (Mokhtaran, Fakharyan, Jalilvand, & Mohebi, 2015).
Jaramillo, Mulki, and Solomon (2006) focused on role theory, in which he described that the role theory defines that the employees become dissatisfied & their performance when expected behaviours from employees are inconsistent, and same situation will occurred when the individual perceives that his job duties are not clear and ambiguity which include role, responsibility and reporting officer, the unclear duties or role ambiguity create conflicts among employees which will ultimately effects on output of organization, beside this role ambiguity create stress for employees and fail to perform their duties in effective way or according to their ability and capacity, and with the passage of time he will consider to quit the organization.
2.1.2. Relevant Nature of Work
Relevant nature of work means the appointment of the right person, at right place and at right time. Employees prefer to work in their specialized fields which give them opportunity to use their skills and abilities to get positive feedback from their team leader (Lumley et al., 2011).
Most of the organizations assign those tasks to their employees who are not relevant to their fields or interests or beyond their capacity, and this situation creates dissatisfaction among employees but employees feel comfortable and perform much better assigned task if he work in his specialized field (Ho, Chang, Shih, & Liang, 2009).
The teamwork creates the constructive work climate in the organization, through which the management can easily improve the performance of employees through establishment of open door communication between management and employees which help to management to knowing employees by name, get quick response and feedback, giving freedom to plan work hours or freedom to choose the way to complete the work or giving an autonomy, giving value and recognition to employees against their performed work , this constructive work climate build the trust and create sense of responsibility and loyalty among employees in the organization, and at the same time, it creates the sense of high morale of employees in the organization, which ultimately increase the employees performance as well as satisfaction (Richardson, 2008).
2.1.4. Rewards
Chiew and Braver (2014) explained that rewards consistently enhance a proactive type of thinking toward job satisfaction and exerting a robust in his performance.
The employee must be satisfied with appreciation, recognition and reward in shape of bonus or extra benefit for performing task full commitment and dedication. Rewards are recognition of employee’s performance; employees feel dissatisfaction whenever their efforts are not recognized and they feel that they are not treated as fair (Lumley et al., 2011).
2.1.5. Fairness
Performer employees are always very much conscious about fairness of procedures and policies at work environment, it affects their intention and emotions when they are treated unfair such as anger, guilt, dissatisfaction and others, but when they are treated fair on basis of their output then they feel satisfaction and show their full loyalty & commitment and desire to stay further in the company (Irshad & Afridi, 2007).
2.2. Perceived Performance
Performance is linked with job satisfaction and job satisfaction does not come in isolation but it is level of degree between individual and organization, it is dependent on different variables of organization such as pay, size, structure, leadership and organizational working condition and climate, the individual with high level of job satisfaction shows his positive attitudes and perform his assigned assignments with full motivation towards achieved organizational goals whereas the dissatisfied individual will show his negative attitudes in his assigned tasks (Lumley et al., 2011).
According to Tsai (2014) performance is based on job satisfaction whereas job satisfaction is strongly associated with types of organization and work climate of organization, he argued that positive climate of organization is connected with improved performance through higher point of job satisfaction along with lower rate of turnover.
Putter (2010) he argued that the improvement in employee performance and success of organization is mostly dependent on the efforts of human resources throughout the world, and knowledgeable, flexible and productive employees in the organizations are main source of firm sustainability in competition or human resources is competitive advantage of organization in these days, thus, management of firm is continuously recognizing that human resources of organization build the difference and create value of company in the market.
Tsai (2014) define organizational climate as perception of employees regarding organizational features such as norms at workplace, decision making, formal policies of organization, employee value and importance, employee needs, employee personalities and others, basically, organizational climate is combination of different characteristics, and positive climate considered to enhance the motivation of employee in which employee takes extra efforts in his assigned tasks, positive climate is strongly connected with improvement of performance.
Scholars have examined the connection between satisfaction of employee and a number of human resources outcomes, and it was found that satisfaction of employee drives productivity in the organization, and key factors in development of better environment for satisfaction of employees are increase morale support and recognition, pay raises, overtime, gain sharing, bonuses and others, therefore practices of human resources should be understand and worked out as antecedents in the direction of organizational effectiveness (Chang & Huang, 2010).
Attridge (2009) he said that, to improve performance of employees in the organization, decision maker or top management needs to avoid overload or creating complex job demands and stop stressful conditions at work, because these factors develop burnout and exhaustion situations for employee, therefore, it is important that these factors should be converted into better work climate such as role clarity among employees , social relationships activities or events at work, flexibility in work schedule, proper distribution of work load, include workers in decision making process.
The employees provide high standard response when company provide supporting atmosphere like: quality services inside the company’s work climate and providing facilitative conditions which also include efforts towards removing obstacle to work, behaviour of supervisor, basically, the organization are required to create such environment which make employees loyal and enables them to deliver outstanding and better performance or service to their customers as compare to other competitors in the market (Mokhtaran et al., 2015).
Chen, Ployhart, Thomas, Anderson, and Bliese (2011) the talent retention become a serious issue for most of the organizations in all over the world from last decade because firstly, it was curtail issue for limited developed countries of the world, and it has observed that demand of talent is continuously increasing day by day, and due to this, the most of the firms have loosed their market share and it is difficult for them to compete with those organizations who have talent; in current scenario of talent war, the firms success is mainly depend on talent which is limited in labour market and the talent mobility from one organization to other organization is depend on job satisfaction in the organization.
The successful organizations are working on philosophy of investing and valuing their employees towards managing retention of their talented or key employees, and talent is consist of those employees who takes organization from bottom to top or help to maximize its profits in tough competition in market (Irshad & Afridi, 2007).The turnover of key employee (critical position) can create huge loss for the organization in terms of time (in searching and hiring of new suitable candidate and training of same), profit and market share (by loosing potential customers who were linked with key employee), disturbance in work climate and flow of productivity (Siebert & Zubanov, 2009).
Just recruitment procedures are not enough to keep new employees in organization for long time, if organization management don’t have strategies or policy for good work climate such as advancement attitudes, effective communication and interaction, collaboration, work groups, then they use to face challenges of retention, therefore, organization should develop retention strategies before hiring new employees because through retention strategy of work environment will lead to high performance and success of work groups and keep employees motivate all the time, in bottom line, the improper retention strategies will develop negative consequences because once you hired employee then you develop his core competency through orientation and trainings which are necessary for achieving his assigned tasks, and once he trained then his value will increase automatically in the market, once his value increase then he looks for different opportunities in other organizations if existing firm don’t provide him conducive work climate to keep him satisfied for all the time, therefore it is necessary to provide the employee good working climate which increase his commitment with organization and work with full potential and don’t think to leave the organization (Richardson, 2008).
According to Medina (2012) employee turnover can be easily predicted by focusing comprehensive measures of work climate towards job satisfaction, In bureaucratic culture organization provides the result of minimum levels of organizational commitment and job satisfaction among employees whereas in supportive cultures and innovative cultures (non bureaucratic culture), it is simple to imagine or visualize that workplace is focused on harmony, respect, pride, trust and productivity, which automatically creates the climate of job satisfaction, there is need that every organization must identify the main and specific climate factors of job satisfaction to keeping in view of market competition and fast paced conditions in market, because turnover of talent causes huge cost for an organization, it includes direct costs by replacing employee and indirect cost pertain to loss of key employee experience, skills and abilities, both costs ultimately decrease the productivity and create tough situation for an company or organization, therefore, it is necessary to avoid voluntary turnover and put extra efforts on talent retention which will give benefits to company.
Stewart (2011) the talent always looks and encourage by fairness in terms of moral, just, respect and fair with everyone in the organization, the organization must ensure proper implementation of fairness otherwise organization may bear huge loss of money for conducting exist interview, pay all due allowances to outgoing employee and recruitment of new employee along with disturbance in flow of work.
Dawson and Abbott (2011) define that throughout the world the importance of talent has accepted and considered that human capital is important resource which can provide potential competitive advantage to organization in global market, whereas it is more important for those organizations who are providing services means include in the definition of service sector such as banking industry, hospitality industry and others.
Today’s intelligent and smart managers of the organizations recognize that employees are asset of organization and spend on their growth in a encouraging work climate leads to enhance the motivation & job satisfaction as well as reduce the employee turnover in the organization, and now human resources professionals are applying high performance employment/ work practice, and these practices boosts the skills, abilities and knowledge of the existing employees, and increase employee motivation & performance in the process of service delivery and talent retention, if organization avoid to invest in performance of employment then automatically organization lose the talent pool and such loss will create reduction in new ideas and ultimately deliver the poor service to their potential customers (Karatepe & Vatankhah, 2014).
Musser (2008) found that retention is nonstop process and required continuous efforts to maintain it instead of treating it as periodic activity, retention programs and strategies of organizations are different from organization to organization, it is not easy to develop by only members of seniors committee or task force, retention strategies are required a lot efforts in development by top management and professional of human resources department, only development is not sufficient but proper implementation and needed continuous improvement, organization should use proactive approach to gather data or determined the factors which compel employees to stay more in organization before voluntary exit of employees should start in the organization.
Over the previous few decades the economy of china has significantly and rapidly increased in global market because china has harvested cheap labour pool, and today a maximum goods or products sold in world countries are made of china, recently china has left behind the Japan and other developed countries in global competition and as per comments of experts that in coming few decades it will overtake the America (USA), but unfortunately, this high and continuous growth in China has created shortage of talent for a number of organizations, and this shortage of talent is creating problem for China to become economical powerful country in the world (Fu, Deshpande, & Zhao, 2011).
After go through the different previous research studies, it has been noted that there is exhaustive factors list pertain work climate which influence on perceived performance and talent retention in the organizations. According to Cappelli (2008) at its spirit, the management employee perceived performance and stay in organization is just issue of job satisfaction, which means it is matter of anticipating the need in favour of human capital and then fixing out a strategy to meet it.
The conceptual framework of this study is based on following model. In which, work climate is based on five independent variables such as: Role Clarity, Relevant Nature of Work, Teamwork, Rewards & Fairness, and one intervening(mediating) variable which is perceived performance and one dependent variable which is talent retention. The selection of independent, mediator and dependent variables of this study is based on different previous research studies and not only from any particular study, and is focused only on Pakistan environment, where expectations of employees towards job satisfaction are different from other countries, and the impact of factors of work climate are different in percentage on perceived performance and talent retention are also vary from others countries.
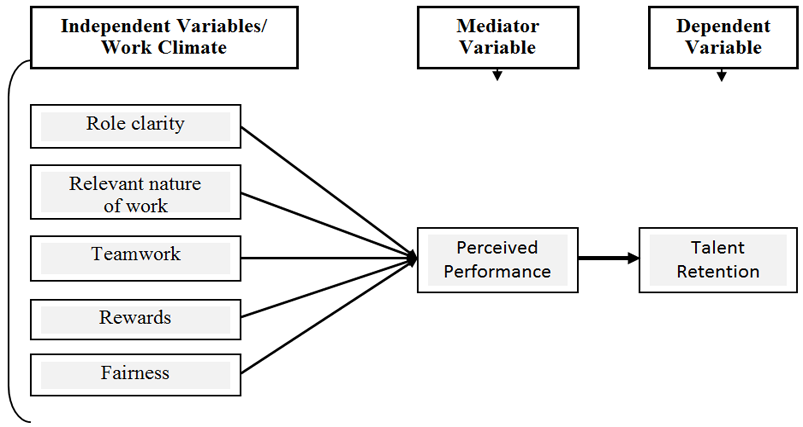
Figure-1. Conceptual Framework.
3. Research Methodology
This study was quantitative in nature and based on the philosophy of positivist and deductive approach were used, in which primary data was collected through conducting survey by using mono method of quantitative technique (structured questionnaires), beside this, the cross- sectional time horizon was taken in this study. In positivist approach philosophy the researcher needs to focus on facts and implement deductive method (Levine & Crowther, 2008).
The population of this study was focused only on Managers Operations of all branches of different commercial banks which were functional and located in Karachi city and the estimated total population is 760 (38X20=760X1=760 (38 operational commercial banks in Pakistan, 20 average branches each bank in Karachi, 1 average head/ manager in operations department)) as detail collected from information centre of State Bank of Pakistan. On basis of population, the sample size of 201 was taken for primary data collection survey through close ended questionnaire after proper calculation at 95% level of confidence with 5% minus plus error (Saunders, 2006). Beside this, the convenience sampling of non probability was used to collect data from participants.
The following were the hypothesis of study:
H1: Role clarity improves the perceived performance leading to talent retention
H2. Relevant nature of work improves the perceived performance leading to talent retention
H3. Teamwork improves the perceived performance leading to talent retention
H4. Rewards improve the perceived performance leading to talent retention
H5. Fairness improves the perceived performance leading to talent retention
H6: There is positive relationship between perceived performance and talent retention
4. Data Analysis
The data analysis has been done by applying different statistical tests by using SPSS
4.1. Reliability
The reliability results of collected data from 201 respondents are shown in Table 1 in which overall reliability (Cronbach Alpha) of tool is 0.929> 0.7 which indicates that there is high internal consistency among the constructs, and beside this individual values of all variables results are between the range of 0.803 to 0.847 >0.7 which also depicting that the scale is adequate reliable to further use for testing of hypothesis.
| Variable | No. of Items |
Chronbach’s Alpha Value |
| Overall Reliability | 35 |
.929* |
| Role Clarity | 5 |
.812* |
| Relevant Nature of work | 5 |
.823* |
| Teamwork | 5 |
.822* |
| Rewards | 5 |
.803* |
| Fairness | 5 |
.847* |
| Perceived Performance | 5 |
.833* |
| Talent Retention | 5 |
.832* |
Note: *Reliability is good at the 0.70>. |
4.2. Correlation Analysis
To check the relationship among variables the correlation test was applied. Results of correlations among variables are shown in Table 2 in which Role clarity’s Pearson correlation value is .588 along with significant value of.000, which indicates that there is enough correlation between Role Clarity (independent variable) and Talent Retention (dependent variable), whereas Fairness has Pearson correlation value is .641 with significant value of .000 which is highest value among all other independent variables which depicts strongest correlation of Fairness (independent variables) and Talent Retention (dependent variable).
All others independent variables such as Relevant Nature of Work, Teamwork and Rewards have Pearson correlation values are .600, .600 and .627, respectively along with significant value is.000, which shows strong correlation of these three variables with dependent variable- Talent Retention. The Pearson correlation value between perceived performance and talent retention is .744 with significant value of .000, which depict that there is high and strongest correlation between perceived performance (intervening variable) and talent retention (dependent variable) in the framework of this study.
Role Clarity |
Relevant Nature of Work |
Team work |
Rewards |
Fairness |
Perceived Performance |
||
| Talent Retention |
Pearson Correlation |
.588** |
.600** |
.600** |
.627** |
.641** |
.744** |
| Sig.(2-Tailed) | .000 |
.000 |
.000 |
.000 |
.000 |
.000 |
|
| N | 201 |
201 |
201 |
201 |
201 |
201 |
Note: **.Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). |
All results found significant .000. This depicts that there is strongly positive relationship between independent variables (i.e. Role Clarity, Relevant Nature of Work, Teamwork, Reward and fairness) and intervening variable (Perceived Performance). Similarly, results also indicated that there is strong and positive relationship between intervening variable (Perceived Performance) and dependent variable (Talent Retention).
4.3. Regression Analysis
For proper and accurate regression analysis, the frame work is divided into two models i.e. Model 1- analysis the impact of independent variables on intervening variable and Model 2 analysis the impact of intervening variable on dependent variable. Firstly, for results of model 1, the regression test is applied between independent variables (i.e. Role Clarity, Relevant Nature of Work, Teamwork, Reward and Fairness) and intervening variable (Perceived Performance), Results are as under:.
Model |
R |
R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
Std Error of the Estimate |
1 |
.776a |
.602 |
.592 |
.59561 |
Note: a. Predictors: (Constant),Role Clarity, Relevant Nature of Work, Teamwork, Rewards, Fairness. |
Model |
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
Regression |
104.832 |
5 |
20.966 |
59.102 |
.000b |
|
1 |
Residual |
69.176 |
195 |
.355 |
||
Total |
174.008 |
200 |
||||
Note:
|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
t |
Sig. |
||
B |
Std. Error |
Beta |
||||
| (Constant) | .238 |
.132 |
1.804 |
.073 |
||
| Role Clarity | .159 |
.072 |
.156 |
2.204 |
.029 |
|
1 |
Relevant Nature of work | .113 |
.078 |
.111 |
1.439 |
.152 |
| Teamwork | .181 |
.077 |
.175 |
2.336 |
.021 |
|
| Rewards | .138 |
.079 |
.133 |
1.755 |
.081 |
|
| Fairness | .328 |
.068 |
.331 |
4.833 |
.000 |
|
Note:
|
Results shows that the Regression Coefficient is F= 59.102 along with significant at .000, which indicates that the overall impact of model is significant. In addition to this R= 0.776 which indicates that the independent variables are impacting on intervening variable which means that 77.6% variance in intervening variable is defined by independent variables (R Square= 0.602), the model explain the t value is significant in majority of independent variables i.e. Role Clarity, Teamwork and Fairness, whereas in case of remaining two independent variables (i.e. Relevant Nature of work and Rewards) the results are insignificant.
Result also indicate that Beta value of Role Clarity is .156 and it is significant at 0.029, it means if Role Clarity increase by 1 then Perceived Performance will increase by 15.6%, whereas Teamwork and Fairness Beta values are .175 and .331 respectively, which are also significant at .021 and 0.000 respectively, it means that if Teamwork and Rewards increase by 1 then Perceived Performance will increase by 17.5% and 33.1% respectively.
Therefore, according to results of research study, the hypothesis Ha1, Ha3 and Ha5 are accepted here which conclude that there is significant impacts of independent variables (i.e. Role Clarity, Teamwork and Fairness) on intervening variable (i.e. Perceived Performance).
Secondly, for the results of Model 2, the again regression test was applied between intervening variable (i.e. Perceived Performance) and dependent variable (i.e. Talent Retention). Results are shown as under:
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std Error of the Estimate |
| 1 | .744a | .553 | .551 | .63594 |
Note: b. Predictors: (Constant), Perceived Performance. |
| Model | Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
| Regression | 99.556 |
1 |
99.556 |
246.167 |
.000b |
|
1 |
Residual | 80.480 |
199 |
.404 |
||
| Total | 180.036 |
200 |
||||
Note:
|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
t |
Sig. |
||
B |
Std. Error |
Beta |
||||
| (Constant) | .496 |
.122 |
4.054 |
.000 |
||
1 |
Perceived Performance | .756 |
.048 |
.744 |
15.690 |
.000 |
Note:
|
Results of model 2 shows that the Regression Coefficient is F= 246.167 along with significant at .000, which indicate that the overall impact of model is significant. In addition to this R= 0.744 which indicate that the independent variables are impacting on intervening variable which means that 74.4% variance in intervening variable is defined by independent variables (R Square= 0.553), the t value of model is significant .000.
Result also indicate that Beta value of Perceived Performance is .744 and it is significant at 0.000,it means if Perceived Performance increase by 1 then Talent Retention will increase by 74.4%,
Therefore, according to results of research study the hypothesis Ha6 is accepted here which conclude that there is significant impact of intervening variable (i.e. Perceived Performance) on dependent variable (i.e. Talent Retention).
Thirdly,the Sobel test is used to check the effect of independent variables on dependent variable through intervening (mediator) variable as it is conceptualized at following model, whereas the results of Sobel test are exhibited as under:
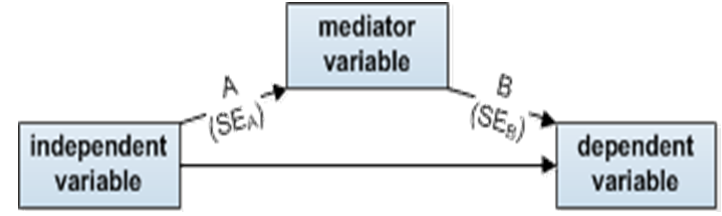
Figure-2. Sobel Framework.
| Variable | Sobel test statistic |
One-tailed probability |
Two-tailed probability Sig. |
| Role Clarity | 2.18694109 |
0.01437341 |
0.02874682* |
| Relevant Nature of Work | 1.44262798 |
0.07456265 |
0.14912530 |
| Teamwork | 2.32489859 |
0.01003869 |
0.02007738* |
| Rewards | 1.73618959 |
0.04126516 |
0.08253032 |
| Fairness | 4.61208639 |
0.00000199 |
0.00000399* |
Note: *Significant. |
Results of Sobel test indicates that there is significant effect of three independent variables (i.e. Role Clarity, Teamwork and Fairness) on dependent variable (Talent Retention) through intervening variable (Perceived Performance), whereas the results of remaining two independent variables (i.e. Relevant Nature of Work and Rewards) are not significant effect, which indicates that in case of these both independent variables there is no impact of intervening variable on dependent variable.
Fourthly, After results of Sobel test the liner regression test was applied again only on those two independent variables (i.e. Relevant Nature of Work and Rewards) which don’t have significant results in Sobel test to check the direct effect of these two independent variable on dependent variable (i.e. Talent Retention). Results are exhibited as under:
Model |
R |
R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
Std. Error of the Estimate |
1 |
.677a |
.459 |
.453 |
.70160 |
Note: a. Predictors: (Constant), , Relevant nature of work, Rewards. |
| Model | Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
1 |
Regression | 82.572 |
2 |
41.286 |
83.873 |
.000b |
| Residual | 97.464 |
198 |
.492 |
|||
| Total | 180.036 |
200 |
||||
Note: a. Dependent Variable: Talent Retention. |
b. Predictors: (Constant), Relevant nature of work, Rewards. |
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
t |
Sig. |
||
B |
Std. Error |
Beta |
||||
1 |
(Constant) | .471 |
.148 |
3.170 |
.002 |
|
| Relevant Nature of Work | .346 |
.071 |
.335 |
4.886 |
.000 |
|
| Rewards | .433 |
.072 |
.411 |
5.992 |
.000 |
|
Note: a. Dependent Variable: Talent Retention. |
Results shows that the Regression Coefficient is F= 83.873 along with significant at .000, which indicates that the overall impact of model is significant. In addition to this R= 0.677 which indicate that these two independent variables(i.e. Relevant Nature of work and Rewards) are directly impacting on dependent variable (i.e. Talent Retention) which means that 67.7% variance in dependent variable is defined by these two independent variables (R Square= 0.459), the model explain the t value is significant at .000.
Result also indicate that Beta value of Relevant Nature of Work .335 and it is significant at 0.000, it means if Relevant nature of Work increase by 1 then Talent Retention will increase by 33.5%, whereas Rewards Beta value is 0.411, which is significant at 0.000, it means that if Rewards increase by 1 then Talent Retention will increase by 41.1%. According to results of research study the hypothesis Ha2, and Ha4 are rejected, and Relevant Nature of Work and Reward have direct relation with Talent Retention and there is no impact or effect of Relevant Nature of Work and Reward on Talent Retention through Perceived Performance as intervening variable.
5. Discussion
This research study was conducted to examine the effects of enhancing work climate to improve perceived performance leading to talent retention; the work clime is consisted of five factors which include Role Clarity, Relevant Nature of Work, Teamwork, Rewards, and Fairness. Beside this it was also important to know which factor of work climate is most important and least important in framework of this study in service sector.
After conducting this study, it is very much clear from the responses of participants which were checked through correlations test that work climate (i.e. Role Clarity, Relevant Nature of Work, Teamwork, Rewards, and Fairness) performs important role to improve the perceived performance leading to talent retention. There is strong and significant relationship among all variables and value of all results were found highly significant as already discussed in data analysis chapter.
Result of this study also explain that, the Fairness is most important factor of work climate towards improved the perceived performance leading to Talent Retention whereas Role Clarity is less important factor of work climate towards improved the perceived performance leads to Talent Retention, whereas Team work value are in between Fairness and Role Clarity.
Jaramillo et al. (2006) has also focused on role theory, in which he describes that unclear duties or role ambiguity create conflicts among employees which will ultimately effects on output of organization. Richardson (2008) has emphasized of teamwork and he explained that the teamwork create the constructive work climate in the organization, through which the management can easily improve the performance of employees. Tsai (2014) he has same positive results in framework of this study where he explained that the performance is based on job satisfaction whereas job satisfaction is strongly associated with types of organization and work climate of organization, he argued that positive climate of organization is connected with improved performance through higher point of job satisfaction along with lower rate of turnover. (Mokhtaran et al., 2015) has defined the similar framework, he explained that the organizations are required to create such environment which make employees loyal and enables them to deliver outstanding and better performance or service to their customers as compare to other competitors in the market.
6. Conclusion
The purpose of this research study was to evaluate the importance of work climate in services sector firms of Pakistan towards improve the perceived performance and examine the how different factors of work climate are impacting on talent retention whether they are effecting directly or indirectly, and which factor of work clime is most important and which one is least important in the organization. After conducting a proper research study, it is very much cleared that the work climate performs important role in service sector towards improve the perceived performance and retention of key person of organization.
Among different factors of work climate, the Fairness is most important factor towards improved the perceived performance leading to Talent Retention, whereas Role Clarity is less important factor towards improved the perceived performance leading to Talent Retention, and Team work is also positively impacting on Talent Retention through Perceived Performance. Whereas other two factors of work climate i.e. Relevant Nature of Work and Rewards are also positively impacting directly towards Talent Retention. Consequently, the organizations pertain to services sector need to understand the importance of five factors of work climate of this study and review these factors continuously to improve the perceived performance and talent retention.
The researcher has achieved useful findings in this research study but keeping in view the importance of topic the following recommendations are given for implementation in business firms:
- This research study accomplished useful findings but there is a room for conducting a comprehensive study to keeping in view of the importance of Perceived Performance and Talent Retention of employees in services sector organizations in Pakistan because now days almost every organization is facing tough competition to achieve their goals.
- Organizations pertain to service sector must understand the importance human resources and work climate towards achieve the organizational goals, therefore organization should define clear role of each employee in the organization to avoid the ambiguity and achieve Perceived Performance leading to talent retention.
- Services sector firms need to understand the importance human resources and work climate towards achieve the organizational goals, therefore organization must create environment of teamwork at work station so that every employee must feels a family type of atmosphere and his importance in the organization, so that he may perform his tasks with full commitment and to stay in organization for longer period.
- Organizations related to service sector are need establish fair policies to deal with employees, and properly implement those policies without any favouritism to any particular employee or group, so that every employee must feel satisfaction of equal treatment in the organization. Fairness in organization encourage employee to work with full dedication and stay more in organization.
- Keeping in view the importance of talent, the employees must be rewarded in monitory term, separately to keep them motivate towards Talent Retention.
- Keeping in view of the importance of talent, every employee must be engaged in his specialized or relevant field at work station which is his main interest to develop his career in actual interest field, this action will always motivate to employee towards Talent Retention.
- This study was limited to five factors of work climate i.e. Role Clarity, Relevant Nature of Work, Teamwork, Reward and fairness, therefore, the organization must also focus on other factors of work climate on other factors of work climate towards improve the Perceived Performance leads to Talent Retention.
Keeping in view the importance of Perceived Performance and Talent Retention of employees, there is great need to conduct a research on other factors of work climate, such as, relaxing office hours, provision of health and fitness facilities (i.e. Exercise gym, Sport activities, Massage and others) because these factors decrease the work stress and keep the employees mentally healthy and satisfied at work.
Further, this study was limited to services sector, therefore there is also need to conduct same type of research study for other sectors because now days management of employees in organizational work climate is equally important for every type of organization due to shortage of talent in market.
References
Attridge, M. (2009). Measuring and managing employee work engagement: A review of the research and business literature. Journal of Workplace Behavioral Health, 24(4), 383-398.
Cappelli, P. (2008). Talent management for the twenty-first century. Harvard Business Review, 86(3), 1-9.
Chang, W. J., & Huang, T. C. (2010). The impact of human resources capabilities on internal customers satisfcation and organizational effectivness. Total Quality Management and Business Excellence, 21(6), 633-648.
Chen, G., Ployhart, R. E., Thomas, H. C., Anderson, N., & Bliese, P. D. (2011). The power of momentum: A new model of dynamic relationships between job satisfaction change and turnover intentions. Academy of Management Journal, 54(1), 159-181.
Chiew, K. S., & Braver, T. S. (2014). Dissociable influences of reward motivation and positive emotion on cognitive control. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(2), 509-529.
Dawson, M., & Abbott, J. (2011). Hospitality culture and climate: A proper model for retaining employees and creating competitive advantage. International Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Administration, 14(4), 289-304.
Elçi, M., & Alpkan, L. (2009). The impact of perceived organizational ethical climate on work satisfaction. Journal of Business Ethics, 84(3), 297-311.
Fu, W., Deshpande, S. P., & Zhao, X. (2011). The impact of ethical behavior and facets of job satisfaction on organizational commitment of Chinese employees. Journal of Business Ethics, 104(4), 537-543.
Ho, W. H., Chang, C. S., Shih, Y. L., & Liang, R. D. (2009). Effects of job rotation and role stress among nurses on job satisfaction and organizational commitment. BMC Health Services Research, 9(1), 8.
Irshad, M., & Afridi, F. (2007). Factors affecting employees retention: Evidence from literature. Abasyn Journal of Social Sciences, 4(2), 307-339.
Jaramillo, F., Mulki, J. P., & Solomon, P. (2006). The role of ethical climate on sales person's role stress,job attitudes,turnover intention,and job performance. Jounal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 26(3), 271-282.
Karatepe, O. M., & Vatankhah, S. (2014). The effects of high-performance work practices on perceived organizational support and turnover intentions: Evidence from the airline industry. Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality & Tourism, 13(2), 103-119.
Levine, M., & Crowther, S. (2008). The responsive bystander: How social group membership and group size can encourage as well as inhibit bystander intervention. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95(6), 1429-1439.
Lumley, E. J., Coetzee, M., Tladinyane, R., & Ferreira, N. (2011). Exploring the job satisfaction and organisational commitment of employees in the information technology environment. Southern African Business Review 15(1), 100-118.
McMullen, T., Scott, K. D., & Royal, M. (2012). Retention of key talent and the role of rewards. World at Work Journal, 21(4), 58-70.
Medina, E. (2012). Job satisfaction and employee turnover intention: What does organizational culture have to do with it. Columbia University, 1-44.
Mokhtaran, M., Fakharyan, M., Jalilvand, M. R., & Mohebi, M. (2015). The effect of service climate on perceived service value and behavioral intentions: The Mediating role of service quality. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 20(4), 472-486.
Musser, L. R. (2008). Effective retention strategies for diverse employees. Journal of Library Administration, 33(1), 63-72.
Olakitan, O. O., & Ayobami, A. P. (2011). An investigation of personality on entrepreneurial success. Journal of Emerging Trends in Economics and Management Sciences, 2(2), 95-103.
Putter, L. (2010). Organizational climate and performance: 'The relation between organizational climate and performance and an investigation of the antecedents of organizational climate.
Richardson, J. (2008). The business model: An integrative framework for strategy execution. Strategic Change, 17(5-6), 133-144.
Saunders, S. (2006). Are quantum particles objects? Analysis, 66(289), 52-63.
Siebert, W. S., & Zubanov, N. (2009). Searching for the optimal level of employee turnover: A study of a large UK retail organization. Academy of Management Journal, 52(2), 294-313.
Stewart, J. (2011). Calculus. Engaged Learning.
Tsai, C. l. (2014). The organizational climate and employees ' job satisfaction in the terminal operation context of kaohsiung port. The Asian Journal of Shipping and Logistics, 30(3), 373-392.